The Underestimated Threat Snoring
What is Snoring? Causes, Effects, and Treatment Options
Snoring is a common issue that affects many people. It is characterized by a vibrating sound caused by the partial obstruction of the upper airway during sleep. But why exactly does snoring occur? What are the factors that contribute to it, and how can it be treated? In this article, we will explore the causes of snoring, its health implications, and the various treatment options available.
What is Snoring?
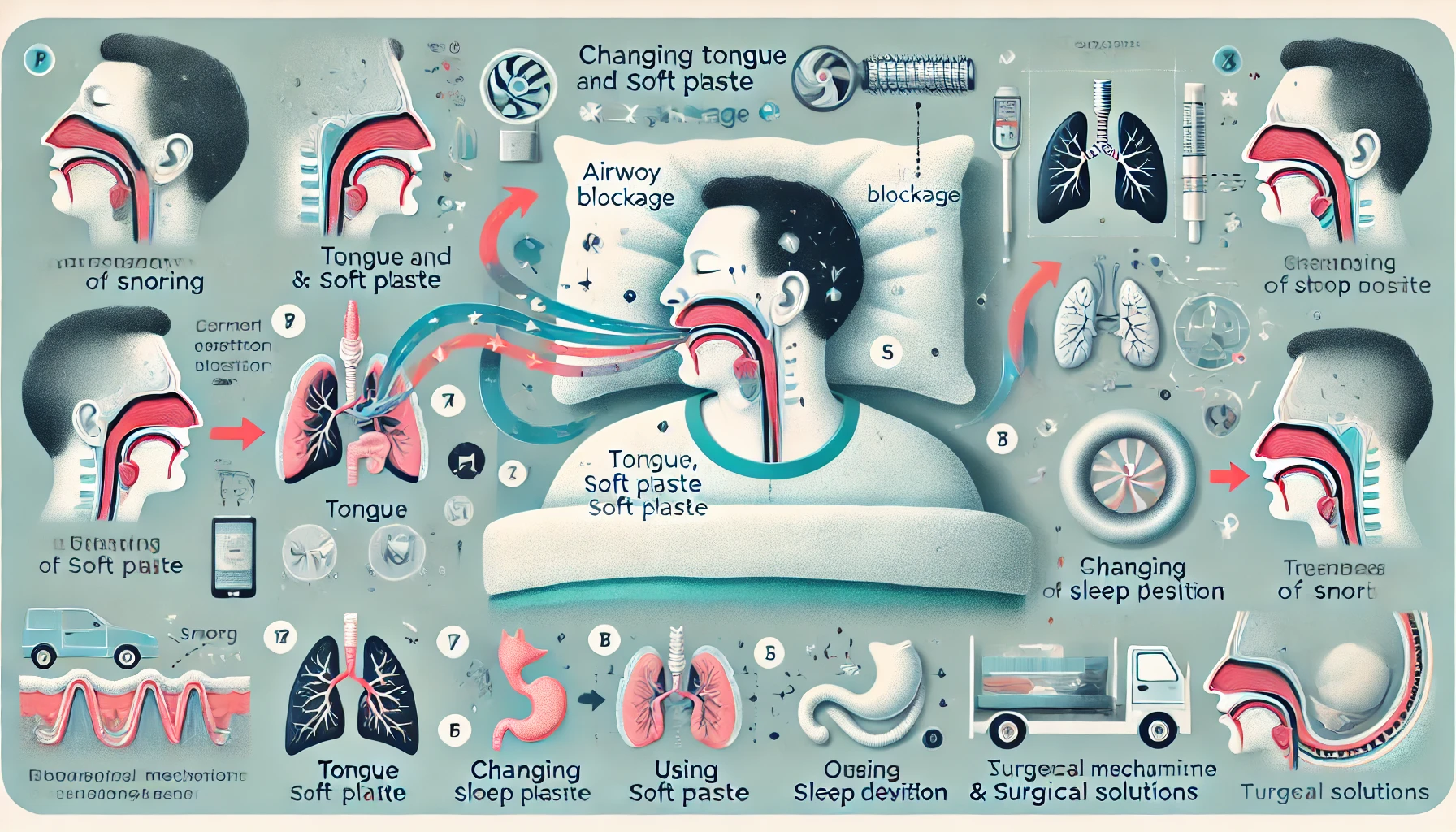
Snoring is a condition that occurs when the airways become partially blocked during sleep, causing a loud, vibrating sound as air flows through. The narrowing of the upper airways restricts airflow, which leads to the vibration of soft tissues, producing the characteristic snoring noise. While snoring may seem like just a social inconvenience, it can often signal underlying health issues.
The Physiological Mechanism of Snoring
Snoring is caused by the vibration of soft tissues in the upper airway, such as the throat, tongue, and soft palate, as air passes through during sleep. As these tissues relax during sleep, they may partially obstruct the airway. This partial blockage forces air through a smaller passage, causing the tissues to vibrate and create the snoring sound.
People who snore often wake up feeling tired because snoring can interrupt oxygen flow to the brain. It reduces sleep quality and can result in both physical and mental fatigue.
Causes of Snoring
Snoring can result from various factors. Here are the primary causes:
1. Anatomical Factors
Anatomical structures play a major role in causing snoring. Common anatomical causes include:
- Enlarged tonsils
- Elongated soft palate
- Large tongue
- Deviated nasal septum
These structural abnormalities can narrow the airway, making it more difficult for air to pass through and causing snoring.
2. Sleep Position
Your sleep position can significantly impact snoring. Sleeping on your back allows the tongue to fall backward, which can obstruct the airway and increase snoring. Sleeping on your side, however, helps keep the airway open and reduces snoring.
3. Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle habits like alcohol consumption, smoking, and obesity can also increase snoring. Alcohol and smoking relax the muscles in the throat, leading to a narrowed airway. Additionally, excess weight can contribute to increased fat tissue around the neck, which further narrows the airway.
The Health Effects of Snoring
Snoring is more than just a nuisance; it can also have significant health implications. Here are some of the main health effects associated with snoring:
1. Impact on Sleep Quality
Snoring can be a symptom of sleep apnea, a serious sleep disorder. Sleep apnea causes short interruptions in breathing during sleep, leading to poor sleep quality and resulting in daytime fatigue.
2. Relationship with Cardiovascular Diseases
Snoring has been linked to several cardiovascular issues, including high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke. This connection highlights the potential health risks that snoring can pose if left untreated.
3. Social and Psychological Effects
Snoring can cause disruptions not only for the person snoring but also for their partner. Disrupted sleep patterns can strain relationships and lead to frustration. People who snore may also experience embarrassment or low self-esteem in social settings.
Treatment Options for Snoring
The treatment for snoring depends on the underlying cause and its severity. Here are some effective methods to reduce or eliminate snoring:
1. Changing Sleep Position
One of the simplest ways to reduce snoring is by sleeping on your side. Sleeping on your back causes the tongue to fall backward, blocking the airway, while sleeping on your side keeps the airway more open.
2. Lifestyle Changes
Making lifestyle changes can significantly reduce snoring. Limiting alcohol and smoking, losing weight, and engaging in regular exercise can all contribute to less snoring. Avoiding heavy meals before bedtime may also help keep the airway clear during sleep.
3. PAP (Positive Airway Pressure) Devices
PAP devices, including CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure) and BPAP (Bi-level Positive Airway Pressure), are commonly used to treat both snoring and sleep apnea. These devices work by providing a steady stream of air pressure through a mask, keeping the airway open and preventing snoring.
4. Surgical Interventions
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to correct anatomical issues that cause snoring. Procedures can involve reshaping tissues in the soft palate or throat to widen the airway. Skilled surgeons, like Dr. Sema Koç, perform these procedures with high success rates, offering long-term solutions to snoring.
5. Success Rates of Snoring Surgery
Surgical interventions, when performed correctly, can significantly reduce or eliminate snoring. However, the experience of the surgeon plays a key role in achieving successful results. Dr. Sema Koç has a high success rate in snoring surgeries, with many patients achieving permanent relief from snoring.
The Role of Revision Surgery
In some cases, the initial snoring surgery may not provide the desired results, and revision surgery may be required. Revision surgery addresses issues that remain after the first surgery, providing a more comprehensive solution to the problem.
Dr. Sema Koç is also highly experienced in revision surgery, offering effective solutions for patients who have not achieved success with their initial procedures.
Recovery Process After Snoring Surgery
1. Post-Surgery Care
After snoring surgery, it is important to rest and follow your doctor’s instructions for a smooth recovery. During the first few days, there may be some swelling or discomfort, but these symptoms usually subside quickly.
2. Tips for Accelerating Recovery
- Stay hydrated, as it helps speed up the healing process.
- Maintain a healthy diet and avoid smoking to support tissue repair.
- Keep your head elevated while sleeping to reduce post-surgery swelling.
Conclusion: Is Snoring Surgery a Permanent Solution?
Yes, snoring surgery is generally considered a permanent solution. Surgical interventions address the anatomical causes of snoring, keeping the airway open and reducing or eliminating snoring altogether. However, maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial to ensure long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What causes snoring?
- Snoring occurs when the upper airway is narrowed, preventing air from flowing freely.
- Is snoring surgery a permanent solution?
- Yes, snoring surgery typically provides a long-term solution by correcting the underlying anatomical issues.
- What should I do after snoring surgery?
- Follow your doctor’s post-surgery instructions, eat a healthy diet, and stay hydrated for a smooth recovery.
- Is snoring surgery painful?
- You may experience mild discomfort after the surgery, but it can be managed with pain relievers.
Choosing an experienced and reliable surgeon for rhinoplasty increases the success and safety of the surgery. Learning about your surgeon’s past successes, patient reviews, and portfolio can help you make the right choice. Additionally, maintaining open communication with your surgeon during the pre- and post-surgery processes to clarify your expectations and possible outcomes is important. In this respect, Associate Professor Dr. Sema Koç, with her 22 years of experience, successfully performs her surgeries. You can access her previous surgeries on her Instagram and website.
For more information about nose aesthetics and to schedule a consultation with Assoc. Prof. Dr. Sema Koç, you can contact our clinic.
Other Languages
Author