Does Adenoid Enlargement Cause Snoring?
🩺 Introduction
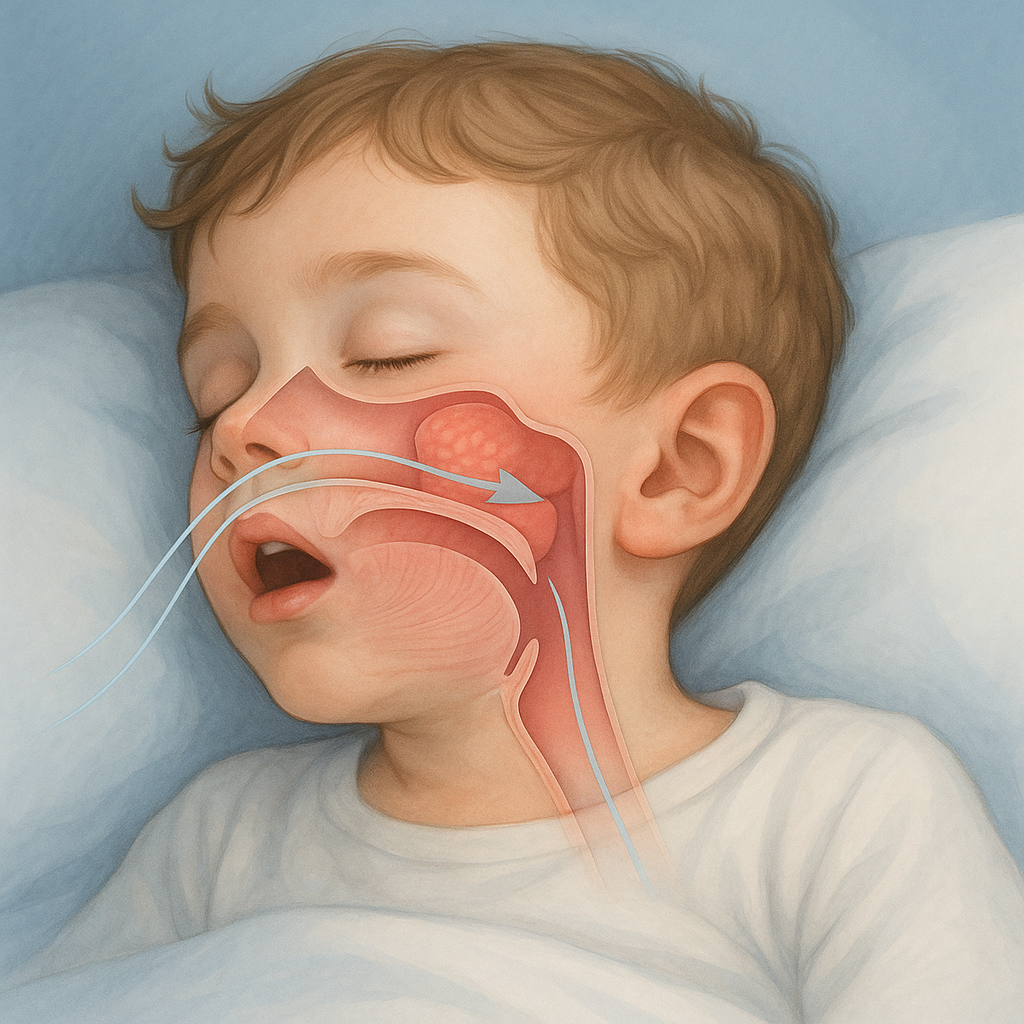
Snoring is more than just an annoying nighttime noise — it can be a sign of a medical condition. One common cause, especially in children, is adenoid enlargement, which blocks nasal airflow.
🔍 What Is the Adenoid?
The adenoid is a lymphatic tissue located behind the nasal cavity. It helps fight infections, but when it becomes enlarged, it can obstruct breathing.
😴 How Adenoid Enlargement Causes Snoring
When the adenoid grows excessively, it narrows the airway and makes nasal breathing difficult. As a result, the person starts breathing through the mouth during sleep, leading to:
-
Snoring
-
Sleep apnea
-
Restless sleep and daytime fatigue
In children, signs include mouth breathing, restless sleep, nasal voice, and frequent ear infections.
⚕️ Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the size of the adenoid:
-
Medication: Used for allergy or infection-related swelling.
-
Surgery (Adenoidectomy): Recommended when the tissue severely blocks airflow.
After surgery, breathing improves and snoring typically disappears.
💡 Conclusion
Yes, enlarged adenoids can cause snoring. However, with early diagnosis and proper treatment, patients can enjoy clear breathing and restful sleep.